Top 10 Fastest Healing Body Parts

The human body has a remarkable capacity for self-healing from wounds and injuries. However, healing takes time in different parts of the body. A few tissues have more blood supply, oxygen and supplements than others, which assist them with recovering quicker. Different elements that influence recuperating speed incorporate the area, size and sort of the injury, the presence of contamination and aggravation, and the general wellbeing and way of life of the individual. We’ve also published article on best food for health
In this article, we will take a gander at the main 10 quickest recuperating body parts, in light of the typical time it takes for them to mend from minor wounds.
10 Fastest Healing Body Parts
- Cornea
- Mouth and Tongue
- Fingers
- Upper Torso
- Face
- liver
- Lung
- Hair
- Skeletal system
- Skin Cells
1. Cornea
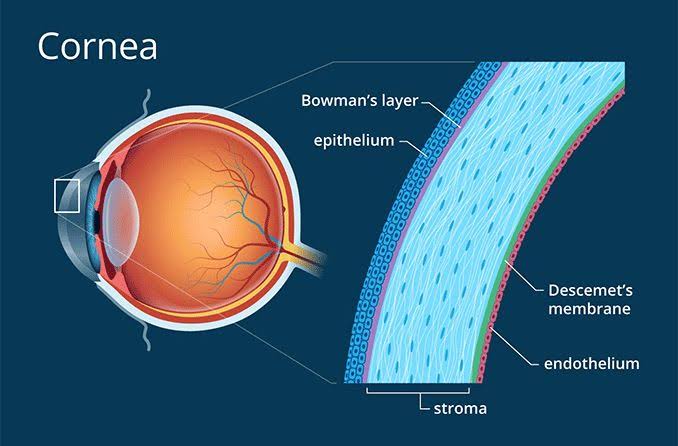
The cornea is the reasonable, vault molded external layer of the eye that assists us with seeing obviously. It gets oxygen directly from the air and doesn't have any blood vessels. Most corneal abrasions heal within 24 to 36 hours, making it the body's fastest-healing tissue. However, larger or deeper cuts may require medical attention and take longer to heal.
2. Mouth and Tongue

The mouth and tongue are likewise among the quickest recuperating body parts, as they have a rich blood supply and a wet climate that forestall disease and scarring. Small cuts or ulcers in the mouth typically heal within a week or less because the mouth heals much faster than the external skin. The tongue can likewise recuperate rapidly from chomps or consumes, as it has a high turnover of cells that supplant the harmed ones.
3. Fingers
Fingers are another body part that recuperates quickly, on account of their bountiful blood course and sensitive spots. Fingers can recuperate from cuts, consumes, rankles or nail wounds surprisingly fast or weeks, contingent upon the seriousness of the harm. Fingertips might actually regrow on the off chance that they are cut off, the length of a portion of the nail bed stays in salvageable shape.
4. Upper Torso
READ ALSO » 8 Easy Ways To Deal With Body Acne
The upper middle, which incorporates the chest, back and shoulders, is likewise a quick mending region of the body. The skin on the upper middle is thicker and more versatile than different pieces of the body, which assists it with opposing contamination and scarring. Additionally, the upper torso has a lot of surface area and a lot of blood, making it easier to close wounds and repair tissue there.
5. Face
Another part of the body that heals quickly is the face, especially from superficial wounds like cuts, bruises, or acne. The face has a high thickness of veins and sebaceous organs that give oxygen and dampness to the skin. Additionally, the face has a lot of fibers made of collagen and elastin that give it strength and flexibility. Be that as it may, further or bigger injuries on the face might take more time to recuperate and leave scars.
6. Liver
One of the most important organs in the body is the liver, which is responsible for detoxification, metabolism, digestion, and immunity. Because it is capable of regenerating itself after being damaged by disease, alcohol, or drugs, the liver is also one of the body's most resilient organs. The liver can bounce back to its unique size and capability regardless of whether up to 75% of it is taken out or obliterated. Nonetheless, constant or serious harm to the liver can weaken its capacity to mend and prompt liver disappointment.
7. Lung
Another organ that can recover from minor infections or injuries is the lung. The lung has a huge surface region and a slim layer that permit gas trade between the air and the blood. The lung likewise has specific cells called alveolar macrophages that unmistakable out unfamiliar particles and microorganisms from the aviation routes. Within a few weeks or months, the lung can recover from acute conditions like pneumonia or bronchitis. Be that as it may, persistent or extreme harm to the lung can cause scarring and loss of capability.
8. Hair
Hair isn't in fact a living tissue, yet rather a protein fiber that outgrows hair follicles in the skin. Depending on genetics, nutrition, and hormones, hair grows at about 0.5 inches per month on average. Hair can also grow new hair and shed old hair to repair damage from heat, chemicals, or styling tools. Notwithstanding, hair development can be impacted by conditions like alopecia (balding), hirsutism (unreasonable hair development) or trichotillomania (hair pulling jumble).
9. Skeletal System
The body is supported and protected by the skeletal system, which is made up of bones, cartilage, ligaments, and tendons. By forming a callus—a mass of new bone tissue—around the injured area, the skeletal system can heal from fractures, sprains, and strains. The callus then restructures itself to restore the bone or connective tissue's original shape and strength. Nonetheless, the mending system can differ contingent upon the kind, area and seriousness of the injury, as well as the age and strength of the individual. You can also read on causes of mental disorder
10. Skin Cells
Skin cells are the most bountiful and often supplanted cells in the body. The skin is made out of three layers: the epidermis (the peripheral layer), the dermis (the center layer) and the hypodermis (the deepest layer). The epidermis is continually shedding dead skin cells and supplanting them with new ones. The epidermis can mend from minor injuries like cuts, scratches or consumes inside a couple of days or weeks, contingent upon the size and profundity of the injury. In any case, further or bigger injuries can harm the dermis or hypodermis, which can take more time to mend and leave scars.
Conclusion
READ ALSO » 7 Reasons Your Body Is Weak And Tired
The human body has a remarkable capacity for self-healing from wounds and injuries. However, healing takes time in different parts of the body. A few tissues have more blood supply, oxygen and supplements than others, which assist them with recovering quicker. Different elements that influence mending speed incorporate the area, size and kind of the injury, the presence of disease and irritation, and the general wellbeing and way of life of the individual. Depending on the extent of the damage, these body parts can recover from minor injuries within a few days or weeks. However, larger or deeper wounds may require medical attention and take longer to heal.
