Top 10 Most Long-Lived Empires In History

In simple words, an empire is a political entity that exerts control or dominance over other political entities and peoples. The world has had empires almost since the beginning of human history. Several empires have achieved global status, with territory spanning more than one continent. History has also shown that some empires last longer than others. Some last just a few years, while others last centuries.
There have even been empires that have lasted more than a millennium. Below are brief descriptions of the ten most long-lived empires in history.
1. Roman Empire (27 BCE – 1453 CE)
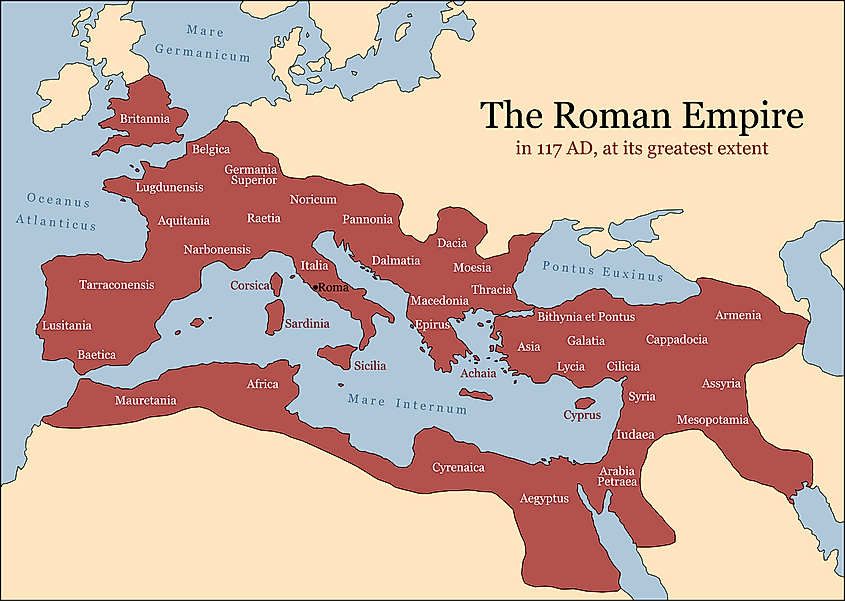
The Roman Empire was the longest-lived empire in history. It officially became an empire in 27 BCE, after civil wars resulted in the collapse of the Roman Republic. By the time Rome became an empire, it already had territory throughout Western Europe, Southern Europe, and North Africa.
Eventually, the Roman Empire got so big that in the 3rd century CE, its emperor, Diocletian, divided it into two units, the West Roman Empire and the East Roman Empire. In 476, the West Roman Empire fell. However, the East Roman Empire endured until the 15th century CE, being referred to as the Byzantine Empire. The Byzantine Empire came to an end in 1453 CE, when the Ottoman Turks conquered its capital, Constantinople.
2. Kush Empire (1069 BCE – 330 CE)
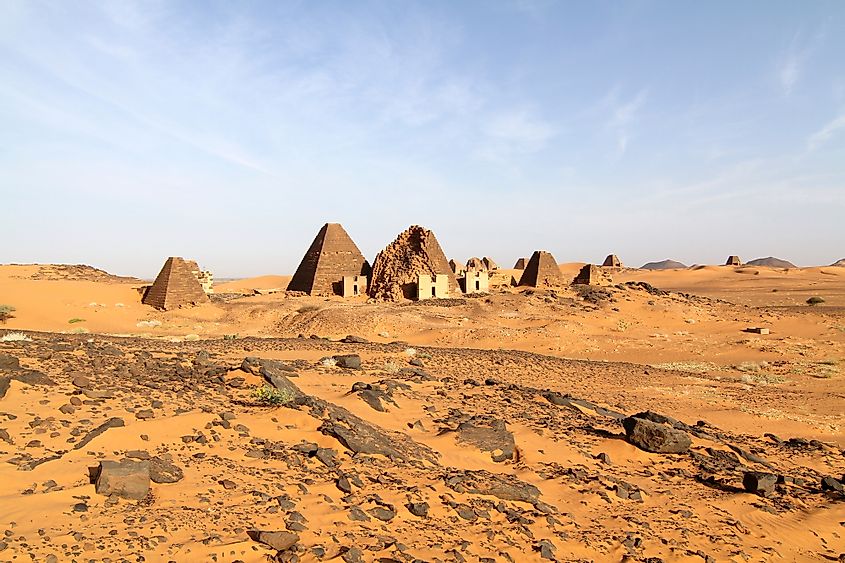

The Kush Empire was based mostly in what is now northeastern Sudan. It began as the city-state of Napata, which later became the capital of the Kush Empire. In the 8th century BCE, Kushite kings became the pharaohs of Egypt’s 25th dynasty. The Kushites, however, lost control of Egypt in 666 BCE, when the Assyrians invaded. In c. 590, Napata was sacked by the Egyptians, and the Kushite capital was moved to Meroe. In c. 330, the Aksumites destroyed Meroe and ended the Kush Empire.
3. The Holy Roman Empire

READ ALSO » Top 10 Famous And Powerful Kingdoms/Empires In Africa
The Holy Roman Empire was an attempt by some leaders in Western Europe to recreate the Roman Empire that had collapsed more than three centuries earlier. It began when Pope Leo III crowned Charlemagne emperor of the Roman Empire. At its peak, the Holy Roman Empire was made up of present-day Germany, Switzerland, Liechtenstein, Luxembourg, the Czech Republic, Austria, Slovenia, Belgium, the Netherlands and large parts of modern Poland, France and Italy.
However, after the Thirty Years War ended in 1648, the empire became fragmented. Finally, in 1806, Napoleon of France forced the last Holy Roman Emperor, Francis II, to abdicate.
4. Republic Of Venice (797 CE – 1797 CE)
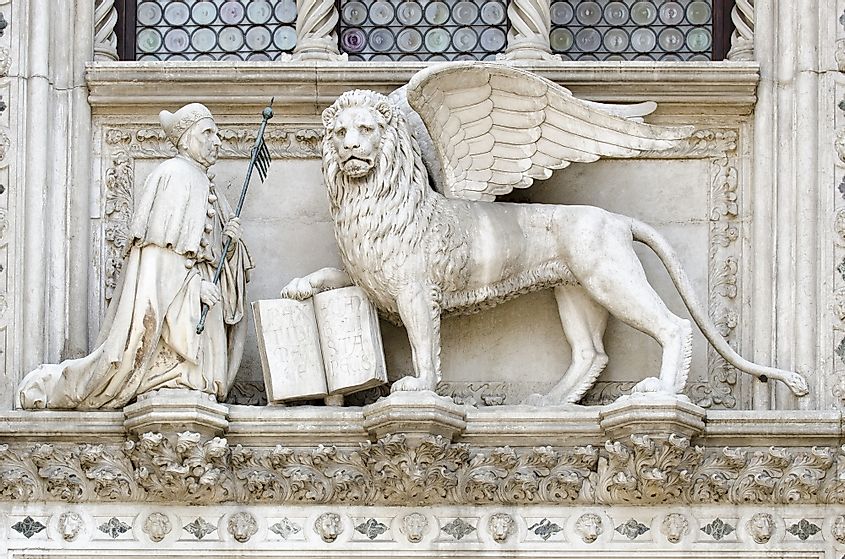

Detail of the Porta della Carta entrance to the Doge's Palace in Venice, Italy, depicting Doge Francesco Foscari kneeling before the Lion of St. Mark, the historical symbol of the Venetian Republic.
The Republic of Venice lasted for a thousand years. The Venetians went on to control territory in Italy’s interior, adjacent to Venice’s core territory, and territory in present-day Croatia and Albania. The primary instrument of the republic’s expansion was its powerful navy. The Republic of Venice came to an end when France’s Napoleon seized the city of Venice itself in 1797.
5. Silla Empire (57 BCE – 935 CE)
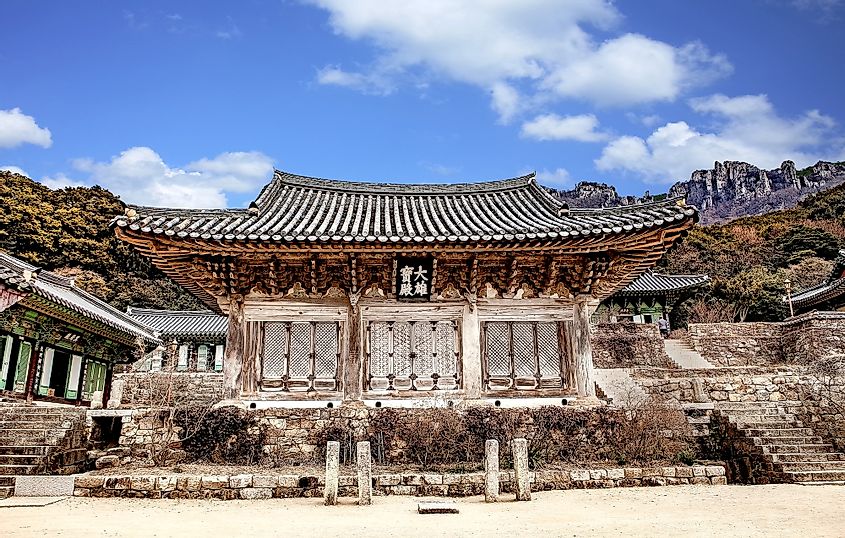

Mihwangsa Temple constructed during the eighth year of King Gyeongdeok of the Silla Dynasty (749), in Haenam-gun, Jeollanam-do, South Korea. The Silla Empire was based in what is now South Korea. It began as a small kingdom in the southeastern region of the Korean Peninsula. The kingdom began expanding slightly in the 1st century CE.
However, it was in the 6th century CE when the expansion of Silla really took off. By the mid-to-late 7th century, Silla and its vassals were the only remaining Korean kingdom, controlling the territory roughly corresponding to present-day South Korea. By the late 9th century, however, the empire began to decline. Finally, in 935 CE, the kingdom was conquered and absorbed by the kingdom of Goryeo.
6. Kanem Empire (C. 700 CE – 1396 CE)
The Kanem Empire was established around the 8th century CE, in an area that now comprises parts of the present-day countries of Chad, Libya, Niger, Nigeria, and Cameroon. It reached the peak of its territorial expansion in the 13th century, though this expansion did not last long, and by the mid-13th century, the realm was reduced to what was more or less its original borders. In 1396, Bulala invaders ended the Kanem Empire by seizing its capital, Njimi.
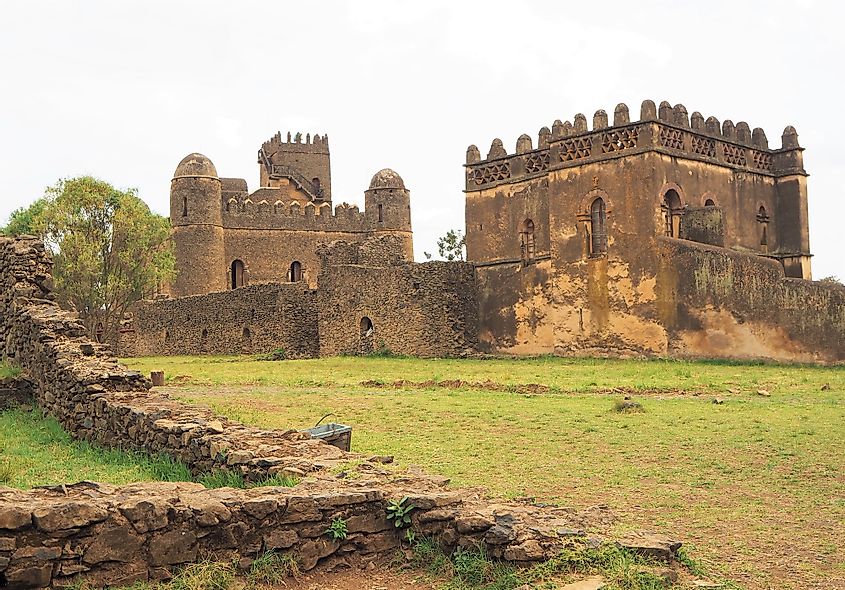
7. Ethiopian Empire (1270 CE – 1974 CE)

READ ALSO » Top 7 Oldest Cats Ever Lived In The World
The Ethiopian Empire began with overthrowing the Aksum Empire’s last dynasty, the Zagwe Dynasty, by the Solomonid Dynasty, which claimed lineage from the Biblical Israelite King Solomon. The Solomonids built an empire by bringing new civilizations within Ethiopia under its rule. Aside from the West African country of Liberia, Ethiopia was the only country in Africa to avoid colonization by European powers.
That is, until Italy invaded and conquered the country in 1936 and ruled it until 1941. The Ethiopian Empire ended in 1974 when a Marxist coup overthrew the last emperor, Haile Selassie.
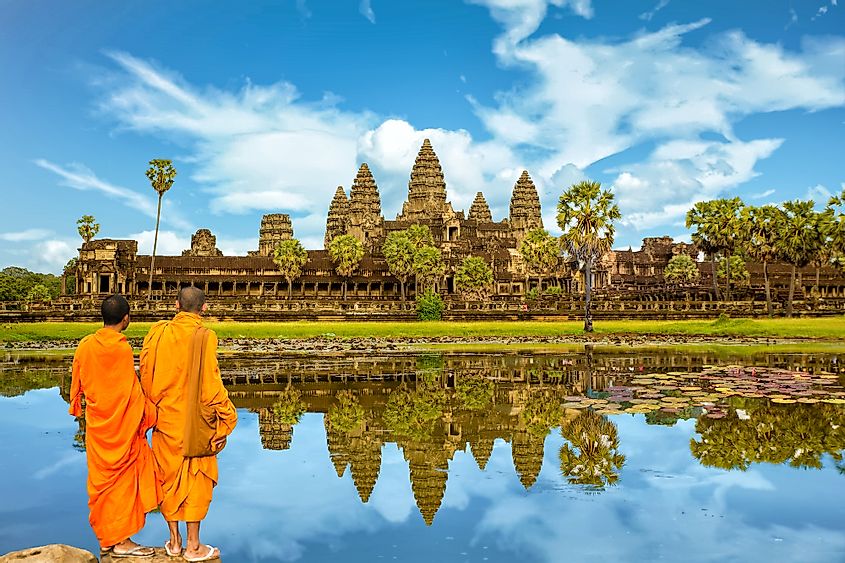
8. Khmer Empire (802 CE – 1431 CE)
The Khmer Empire’s golden age was in the 12th and early 13th centuries. The 12th century was when the great temple of Angkor Wat was built in the Khmer capital, Angkor, which became the biggest pre-industrial city in the world. The Khmer Empire reached its greatest territorial extent in the early 13th century, when it controlled nearly all of Indochina and present-day southern Thailand. But by the mid-13th century, the empire began to decline, threatened by the Tai kingdoms to the west. In 1432, the empire was dissolved, and the Khmer people entered what they refer to as their Dark Age.
9. Ottoman Empire (1300 CE – 1923 CE)
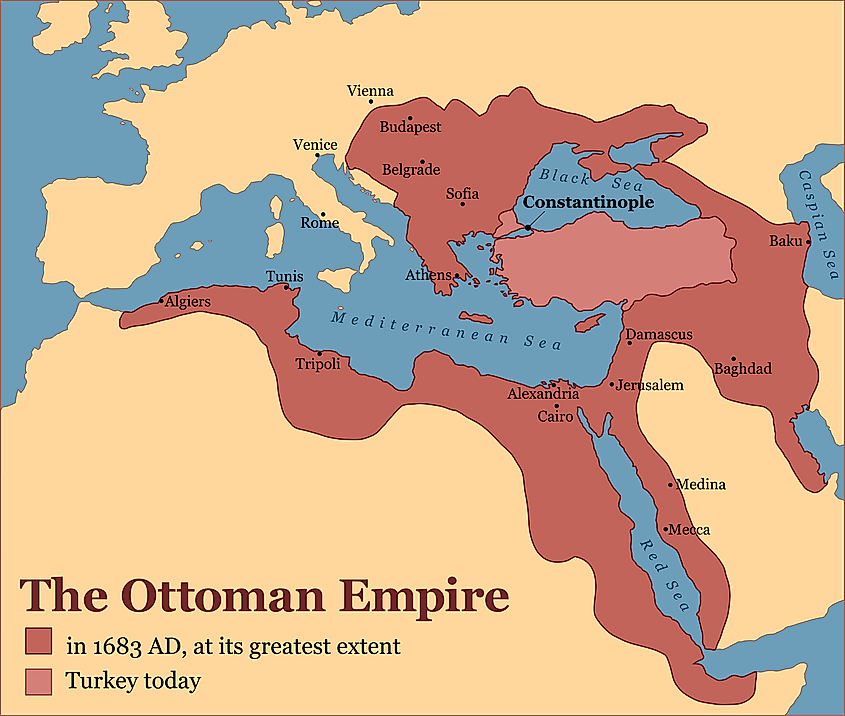
The Ottoman Empire began as a small Turkish state in Anatolia. The Ottoman Turks brought an end to the Byzantine Empire when they seized its capital, Constantinople, in 1453 and made it their capital. At its greatest territorial extent, the Ottoman Empire controlled North Africa, the Balkan Peninsula, and a large part of the Middle East. But by the 18th century, the Ottoman Empire was in decline.
After World War I, the empire was forced to surrender control of its remaining imperial territory in the Middle East. Finally, in 1923, the empire fell and was replaced with the modern Republic of Turkey.
10. Portuguese Empire (1415 CE – 1999 CE)
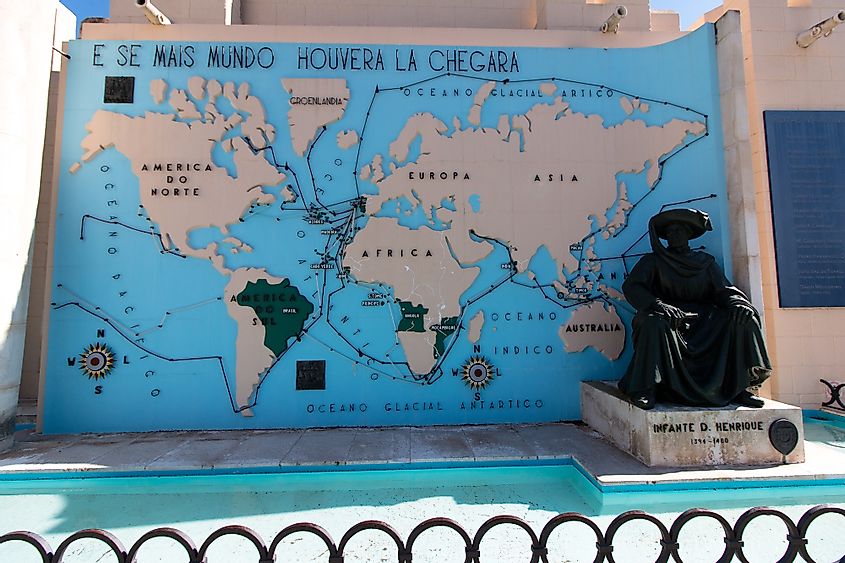
The Portuguese Empire began in the 15th century. At its greatest extent in the 18th century, the empire had colonies in South America, Africa, and Southeast Asia. But in the early 19th century, Portugal lost its largest colony, Brazil. Its remaining, smaller colonies in Africa and Southeast Asia gained independence in the mid-to-late 20th century. In 1999, Portugal gave up its last remaining overseas colony, Macau, to the People’s Republic of China.
